Overview
- User role overview.
- A short introduction to cryptography.
- How to navigate the tiCrypt infrastructure.
Most individuals with a tiCrypt account will be assigned the role of “User”.
Once in tiCrypt, Users can upload files, access approved data, and utilize virtual machines, all with unparalleled security.
Not all Users can access everything in their system.
Admins set the restrictions for each individual User. However, the Users can always view what teams they are on, what projects they belong to, and if they have certifications for specific tasks in their personal profile.
Users can take advantage of tiCrypt functionality to get a feel for the system.
Although tiCrypt was built with security as its primary function, Users will find it easy to treat the system as their own, personal research room. They can view the teams' resources, direct message admins, and even customize the systems theme. tiCrypt offers top-of-the-line security, with a front end that is intuitive for any level of User.
Admins must activate a User’s account before they can access the system.
Introduction to Cryptography
Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure digital communication.
The baseline cryptography technique is the symmetric or “secret key” system. To use this technique, a user converts their data in to a disguised code, called a cipher code. During this process, the user also creates separate a digital key that can reform the cipher code back to its original data. This process of scrambling of data is known as encryption.
The cipher code and the key are then sent to an intended receiver, who can then decrypt the data. The problem with this method is that a third party can intercept the cipher code and the key, thus giving them access to data they shouldn’t have. To address this, cryptologists came up with the asymmetric system.
For this method, every user has both a public and a private key. The public key can be shared, whereas the private key must be protected. A sender requests the public key from the intended receiver, encrypts the message and sends it. When the recipient receives the message, only their private key can be used to decrypt the message. This means that even if a third party intercepted the message, there is no possible way for them to decode it unless they have the recipients' private key.
The following diagram displays how public and private keys from two users can be used for encryption and decryption. Alice and Bob alone cannot encrypt or decrypt. Once they have each other's public key, they can "combine" it with their private key which grants them the "password."
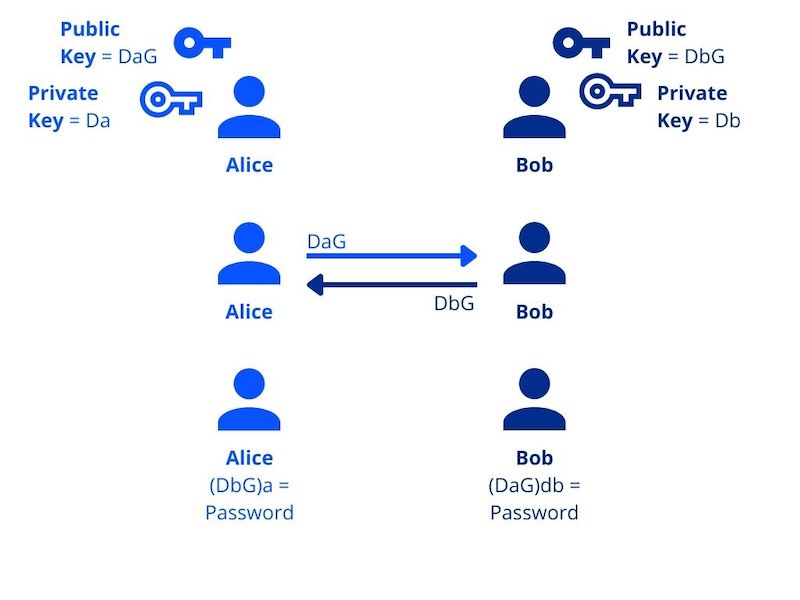
In tiCrypt, every user is given a public and private key. All users must log in to the system using their private key. Every time a user adds a resource to a group, behind the scenes, the user encrypts the resource, and when the recipient wants to view it, they use their private key.
User Infrastructure
View the following video to learn how to navigate in tiCrypt.
The Management tab in tiCrypt is destined for admin roles only.
Now that you know a few things about navigation, we encourage you to try various basic operations initially to learn the basic functions of the system.
Your next step is to follow the Vault Overview section which will allow you to zoom into the user actions.
- Users should act cautiously and intelligently when using tiCrypt. For example, assuming no responsibility when leaving a physical machine open and logged on could lead to a physical breach that may come from the user's lack of care.